Sensitive data is moving through Android healthcare apps without adequate protection. Researchers found that many transmit information without encryption, store files without safeguards, or share it through third-party components.
Study design showing data collection, static security analysis (MobSF, RiskInDroid, OWASP), and sentiment-based review analysis
How the study worked
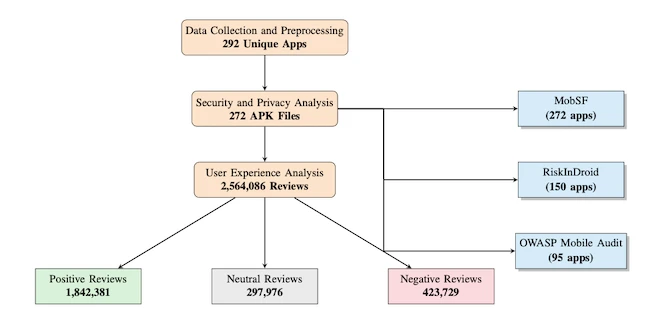
The methodology followed three phases: data collection, security and privacy testing, and user experience analysis.
To gather the sample, the team used twenty targeted search terms on Google Play, including healthcare, medical, fitness tracker, and telemedicine. They took the top thirty results for each term and collected metadata such as app IDs, install ranges, and developer names. They ended up testing 272 apps.
The security and privacy phase used three static analysis frameworks for cross-validation. MobSF disassembled each application’s code and looked for unsafe network settings, weak cryptography, exposed activities or services, and poorly configured manifest files. Findings were mapped to CWE identifiers for comparison with known vulnerability classes.
RiskInDroid analyzed 150 of the apps to map declared permissions against actual API calls, identifying undeclared but used permissions that could act as hidden data channels. It also flagged proprietary permissions by comparing entries to the Android Manifest namespace and checking them against MobSF’s API traces.
OWASP Mobile Audit tested 95 apps using static application security testing rules. It searched for issues such as unencrypted local storage, hardcoded credentials, and missing input validation. Each weakness was classified under the OWASP Mobile Top 10 categories to align results with industry standards.
Findings From MobSF
MobSF assigned each app a score based on security weaknesses in permissions, network handling, certificate management, and manifest configuration. Scores ranged from 35 to 60 out of 100, with an average of 47, suggesting widespread weaknesses rather than isolated flaws.
High-risk permissions were frequent. POST_NOTIFICATIONS appeared in 221 apps, CAMERA in 176, WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE in 204, READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE in 188, and ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION in 146. MobSF also found 529 proprietary or undocumented permissions, usually from third-party SDKs that could access downloads, read device identifiers, or write directly to storage without user awareness.
Network analysis uncovered 22 apps configured to trust all TLS certificates, 42 that allowed unencrypted HTTP traffic, and two that disabled certificate pinning. Cryptographic inspection showed 134 apps vulnerable to the Janus exploit, 58 using SHA1-RSA, and 9 using MD5. Each of these creates openings for interception or tampering with sensitive data.
Results From RiskInDroid and OWASP Mobile Audit
RiskInDroid confirmed that every analyzed app used at least one undeclared permission. Many could send SMS messages, access location data, or alter system settings without explicit consent. More than 100 used account management permissions that could expose user credentials. These permissions often originated from embedded advertising or analytics components.
OWASP Mobile Audit found an average of 44 critical vulnerabilities per app and over 2,000 high-severity issues. Common problems included insecure storage, unvalidated inputs, and weak credential handling. One app contained 299 critical issues, while another exceeded 11,000 high-severity findings. The data suggests that most apps reached users without consistent security testing.
Broader patterns
Users often complained about login failures, password reset errors, and frozen screens. These usability problems tended to occur in the same apps with the weakest security scores, suggesting that poor engineering practices affected both stability and protection.
Across all tools, three trends stood out. First, many developers integrated tracking and advertising libraries that collect more data than necessary. Second, outdated cryptographic algorithms remain common because stores do not enforce minimum standards. Third, default network configurations often remain unchanged, leaving insecure connections active.
The researchers described these as systemic problems caused by fast app deployment, reused code, and limited review during development.
The authors suggest several measures to improve security. App stores could integrate automated scanners such as MobSF and RiskInDroid into submission systems, rejecting apps that fail baseline tests. Developers should use strong encryption, validate certificates, and remove redundant permissions.
Permissions should always match an app’s stated purpose. Undeclared or proprietary ones should trigger review or removal. They also recommend expanding oversight to include wellness apps that collect medical data but fall outside medical regulations.