HONG KONG — As the Trump administration’s immigration crackdown narrows paths to entry for foreign science and technology workers, China is opening its doors wider — and drawing backlash from the public.
The new “K visa,” which launched on Oct. 1, aims to make it easier for the world’s top young talents in science and technology to live and work longer in China as it vies with the U.S. for global dominance in science and technology.
The new category requires no job offer, with the only requirements being an as-yet-unspecified age cap and having at least a bachelor’s degree in science, technology, engineering or math from a top Chinese or foreign university, or relevant teaching or research experience there.
Though many of the details have yet to be announced, the new Chinese visa program is already drawing interest in India, where China is seen as an increasingly appealing destination amid warming relations and the Trump administration’s surprise announcement last month that it is raising the fee for the equivalent H-1B worker visa to $100,000.
Beijing’s talent-friendly move could also give it a boost amid continuing trade tensions and tech rivalries with Washington, which has imposed export controls on chips and other advanced technology that are spurring China to develop its own.
But the new visa scheme has not gone over so well with young job seekers in China, who face intense competition even as universities churn out millions of new graduates a year amid an economic slowdown. Unemployment among people ages 16 to 24, excluding students, was at 17.7% last month, according to government figures released Wednesday.
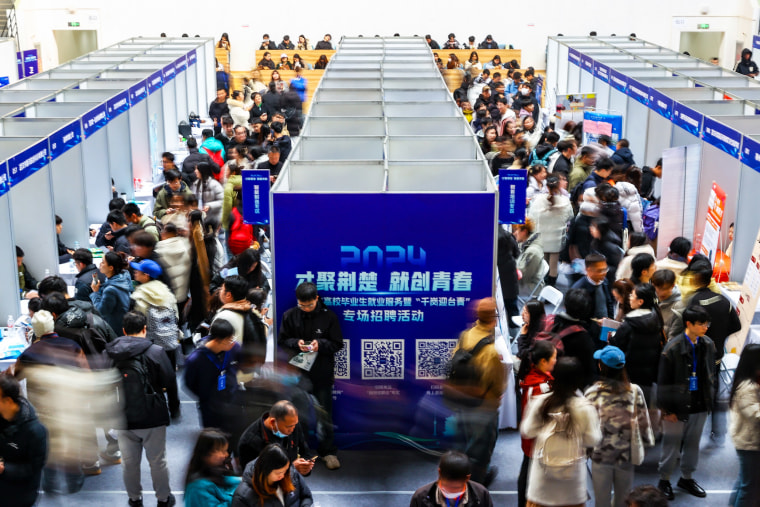

People worry that foreign talents may turn an “already fiercely competitive job market even harsher,” said Geng Xiangshun, a Beijing-based commentator experienced in youth career counseling.
“China already has an abundant, even surplus, supply of highly educated young talent,” Geng wrote in a post on the popular social media platform Weibo. “Since these local talented individuals aren’t even fully employed yet, why do we need to bring in foreign bachelor-degree holders?”
Loosening restrictions
Chinese work visas generally come with strict, complex requirements and allow limited stays for a small group of high-end applicants who are sponsored by employers. Immigrating to China is difficult, and there are many obstacles to living and working there long-term.
Consequently, China is less attractive for foreign professionals than many advanced economies with skilled migration policies, experts say.
Only about 950,000 foreigners work in China, making up just 0.12% of the country’s labor force of about 775 million, according to the Chinese Science and Technology Ministry. In contrast, foreign-born workers accounted for more than 19% of the U.S. civilian work force in 2024, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
The new visa aims to loosen restrictions and enhance China’s global appeal, promising more generous terms such as longer validity periods and multiple entries.
Though China is a relative “latecomer” with this initiative, it represents an “upgrade” to China’s existing talent schemes, said Liu Guofu, a law professor at the Beijing Institute of Technology.
Notably, the new visa does not require employer sponsorship or invitation, resembling “independent skilled immigration,” Liu said.
However, Liu stressed that Beijing’s new talent scheme, which was announced in early August, “bears little direct relation” to President Donald Trump’s shake-up of the H-1B visa fees, which was announced several weeks later.
With the visa’s focus on early-career STEM talents, Beijing is pivoting away from repatriating Chinese scientists and selectively inviting senior foreign experts, said Denis Simon, a leading expert on U.S.-China science and technology affairs.
“By codifying a youth-focused, flexible entry channel, Beijing is normalizing inbound STEM mobility as part of its innovation strategy,” Simon said.
It offers a “lower-friction alternative” for foreign STEM talents who may be frustrated by the higher U.S. fee for H-1B visas, he added, noting that more than 70% of H-1B visa holders are from India.
“Even small diversions of applicants can shift the geography of labs and startups at the margin — precisely where innovation clusters are won,” Simon said.

Public backlash
Beijing’s K visa has been met with strong backlash on Chinese social media, where commenters complained of a lack of transparency and public discussion in policymaking.
Matthew Ma, 18, a freshman majoring in integrated circuits in the eastern Chinese city of Nanjing, said he was “quite surprised” that he had read “nothing” about the new visa in the two months since it was announced.
“The biggest misstep they took in this whole process was not giving out enough information in time,” Ma said. “And this is, I think, the major reason why people are so angry about this visa.”
Others are angered that the visa requires only an undergraduate STEM degree, saying that is setting the bar too low at a time when young people in China feel pressured to rack up advanced degrees in order to compete with their peers in the job market.
Social media has also been flooded with racist and xenophobic comments, especially about Indians, amid fears that an influx of foreigners could erode national identity in China, where the population has fallen for the past three consecutive years.
In a strongly worded editorial last month, China’s state-run People’s Daily newspaper dismissed such concerns as “strange,” “unnecessary” and “misleading.”
“To secure its future, China must attract and utilize the best minds from around the globe,” it said, noting that there is a projected shortage of nearly 30 million skilled workers in the country’s key manufacturing sectors this year alone.
“Such talents are in high demand, and the more we have, the better,” it added. “The K visa is just to facilitate young foreign science and tech talents to work and live in China. It shouldn’t be equated with immigration.”