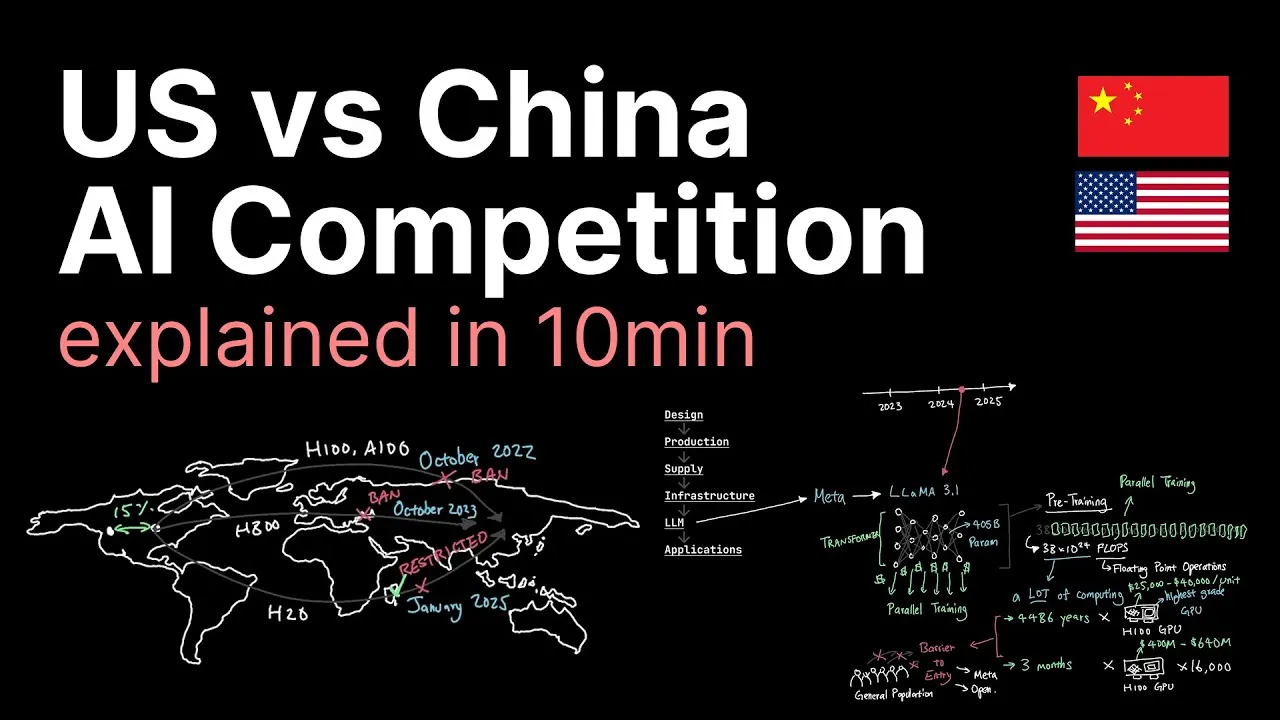
What does it mean when two of the world’s most powerful nations compete over the future of technology? The ongoing US-China rivalry in artificial intelligence (AI) is more than a race for innovation; it’s a contest that could redefine global power dynamics. From the development of new AI applications to the control of critical semiconductor supply chains, this competition touches every corner of the tech world, and beyond. While the United States uses its dominance in infrastructure and innovative hardware, China counters with resourceful strategies and relentless ambition, making this rivalry one of the most consequential battles of the 21st century. The stakes? Nothing less than economic supremacy, national security, and the ability to shape the future of industries worldwide.
In this exploration of the AI competition, Caleb Writes Code uncovers how this technological arms race is unfolding across key domains, from the development of large language models to the strategic bottlenecks in chip manufacturing. You’ll discover how each nation’s unique strengths and constraints are driving innovation, reshaping industries, and influencing global policies. But this isn’t just a story of winners and losers, it’s a glimpse into the forces that will shape the next era of human progress. As we peel back the layers of this high-stakes rivalry, one question looms: will collaboration or competition ultimately define the future of AI?
US-China AI Rivalry
TL;DR Key Takeaways :
- The US-China AI competition is a pivotal 21st-century rivalry, influencing global industries, economies, and national security, with AI applications as the most visible and impactful battleground.
- US companies lead in AI development due to access to advanced computational resources, while Chinese firms innovate with resource-efficient strategies to overcome hardware export restrictions.
- Large language models (LLMs) are a critical and resource-intensive frontier, with US firms using innovative GPUs, while Chinese companies adapt by optimizing older hardware.
- The US dominates AI infrastructure and chip supply chains, with export controls creating significant barriers for China, which is focusing on alternative approaches and domestic semiconductor development.
- The global implications of this AI race extend beyond technology, shaping industries like healthcare and finance, driving economic growth, and influencing global power dynamics in the 21st century.
AI Applications: The Core of the Competition
AI applications represent the most visible and impactful aspect of the US-China AI rivalry. These applications include tools like ChatGPT, AI-driven healthcare diagnostics, and financial forecasting systems, all of which rely on large language models (LLMs). In the United States, companies such as OpenAI, Meta, and Anthropic lead the development of these technologies, while in China, firms like Alibaba and ByteDance are at the forefront.
US companies benefit from access to advanced computational resources, including high-performance GPUs and robust infrastructure. This advantage allows them to develop and deploy AI applications at scale. In contrast, Chinese firms face significant challenges, particularly due to export restrictions that limit their access to innovative hardware. Despite these obstacles, Chinese companies continue to innovate by adopting resource-efficient strategies, such as optimizing algorithms and using alternative hardware. This determination underscores the critical role of AI applications as the focal point of the US-China AI race, where the potential to transform industries is most evident.
Large Language Models: A Resource-Intensive Frontier
Large language models (LLMs) form the backbone of many advanced AI applications, but their development is resource-intensive. Training these models requires immense computational power, advanced GPUs like Nvidia’s H100, and access to vast datasets. US companies often deploy hundreds of thousands of GPUs in state-of-the-art data centers, giving them a significant edge in this domain.
Chinese firms, however, face export restrictions that limit their ability to acquire the latest hardware. Despite this, companies like DeepSeek have demonstrated ingenuity by training models on older or lower-grade GPUs, achieving competitive results through innovative techniques. This approach highlights the importance of adaptability and resourcefulness in overcoming technological barriers. The ability to develop and refine LLMs is a critical factor in maintaining competitiveness in the global AI landscape, as these models drive advancements in natural language processing, machine learning, and other AI fields.
US vs China AI Rivalry Explained
Discover other guides from our vast content that could be of interest on AI Competition.
Infrastructure: A Decisive Advantage
The infrastructure supporting AI development is another key battleground in the US-China competition. The United States holds a clear advantage in this area, with access to advanced data centers and innovative hardware. Export controls on GPUs, such as Nvidia’s H100, have further widened the gap, restricting China’s ability to build comparable infrastructure and limiting its capacity to train and deploy advanced AI models.
Despite these challenges, Chinese companies are finding ways to innovate within their constraints. By optimizing existing technologies, exploring alternative approaches, and focusing on cost-efficiency, they are reshaping the dynamics of AI infrastructure. This resourceful approach demonstrates China’s determination to remain competitive, even without access to the latest tools. The ability to develop robust infrastructure is essential for scaling AI applications and maintaining a leadership position in the global AI race.
The AI Chip Supply Chain: A Strategic Bottleneck
The supply chain for AI chips is a critical factor in the US-China AI competition. The United States dominates this domain, with companies like Nvidia leading the production and distribution of advanced chips. These chips are essential for training and deploying sophisticated AI models. Export restrictions have created a bottleneck for Chinese firms, limiting their access to high-performance GPUs and hindering their ability to compete on equal footing.
In response, China has turned to older or lower-grade GPUs, focusing on maximizing their potential through innovative techniques. While this approach limits performance, it demonstrates resilience and a commitment to advancing AI capabilities despite external constraints. The strategic importance of controlling the AI chip supply chain cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts a nation’s ability to develop and deploy innovative AI technologies.
Semiconductor Manufacturing: The Foundation of AI
Semiconductor manufacturing serves as the foundation of AI development, and the United States holds a significant edge in this domain. Taiwan’s TSMC, a global leader in chip production, relies on extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography technology to produce high-performance chips. However, this technology is unavailable to China due to export restrictions, creating a significant barrier to its semiconductor manufacturing ambitions.
China’s “Made in China 2025” initiative aims to reduce reliance on foreign suppliers by developing domestic semiconductor manufacturing capabilities. However, the lack of access to EUV equipment and other critical technologies presents a formidable challenge. Overcoming these barriers will require substantial investment, innovation, and time. The ability to produce advanced semiconductors is crucial for supporting AI development and maintaining a competitive edge in the global technology landscape.
Global Implications of the AI Race
The US-China AI competition has far-reaching implications for global innovation and leadership. The United States benefits from advanced infrastructure, chip production, and access to innovative technologies, while China’s ability to innovate with limited resources challenges the status quo. This rivalry is not solely about technological superiority; it is about shaping the future of industries such as healthcare, finance, and national defense.
The application layer remains the most critical battleground in this competition. The nation that can harness AI breakthroughs to create impactful applications will gain a significant edge in the global arena. Both the US and China recognize AI’s potential to drive economic growth, enhance national security, and influence global power dynamics. As this competition unfolds, its outcomes will shape the trajectory of technological progress and redefine the balance of power in the 21st century.
Media Credit: Caleb Writes Code
Latest Geeky Gadgets Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, Geeky Gadgets may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.